
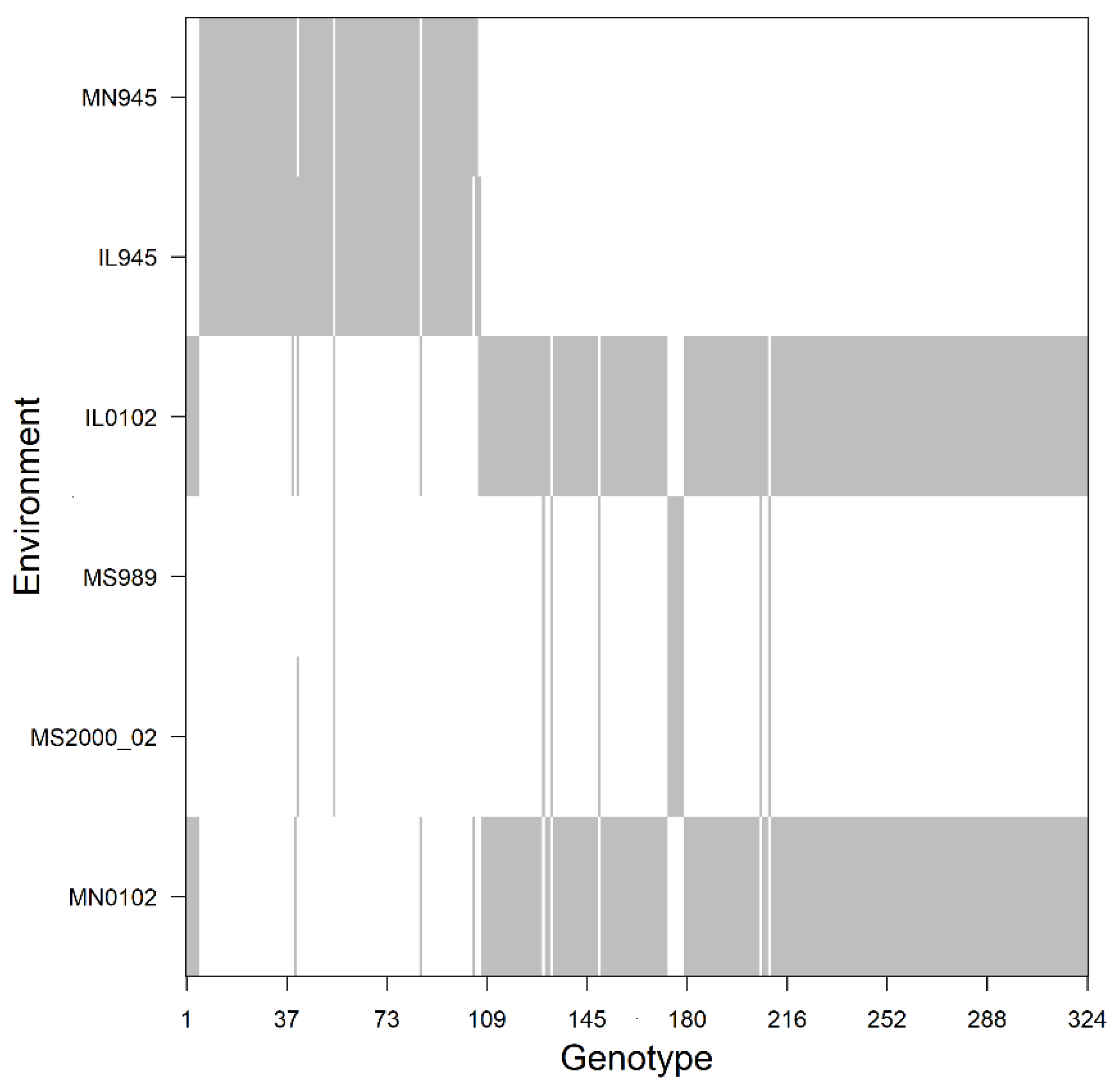

Some examples of monoecious species are corn, squash, banana, and many conifers, particularly those of the genus Pinus. In contrast, dioecious species have distinctive male and female plants. However, several commercial plant species are monoecious, which means that a given genotype will bear both male and female flowers. In most cases it is easy to assign the sex of a given individual. In many plant breeding programs, a parent is considered in several crosses. These BLUPs, which are the general combining ability (GCA), or 1/2 of the breeding value (BV, with BV = 2 ×× GCA) of each parent, are then used to select the best parents for future crosses or operational deployment. The progeny are later evaluated in a field experiment, and this information is used to assess the genetic worth of the parents by fitting parental linear mixed models (LMMs) and obtaining best linear unbiased predictions (BLUPs). xes <- cbind(seq(0, 10, length.Most breeding programs plan several controlled crosses between outstanding parents to detect favorable alleles in their offspring. However, x and y can be specified explicitly. Like plot, if given only one object, matplot assumes it's the y variable and uses the indices for x. Standard graphical parameters, including main, xlab, xmin, work exactly the same way as for plot. matplot(xmat, type = 'l', col = c('red', 'green', 'blue', 'orange')) or a custom vector (which will recycle to the number of columns, following standard R vector recycling rules). However, any (or both) of these aesthetics can be fixed to a single value. Note that, by default, matplot varies both color ( col) and linetype ( lty) because this increases the number of possible combinations before they get repeated. Much more convenient in this situation is to use the matplot function, which only requires one call and automatically takes care of axis limits and changing the aesthetics for each column to make them distinguishable. However, this is both tedious, and causes problems because, among other things, by default the axis limits are fixed by plot to fit only the first column. One way to plot all of these observations on the same graph is to do one plot call followed by three more points or lines calls. Here is an example of a matrix containing four sets of random draws, each with a different mean. Matplot is useful for quickly plotting multiple sets of observations from the same object, particularly from a matrix, on the same graph. Using texreg to export models in a paper-ready way.
PLOT ASREML R TYPE HOW TO
Using pipe assignment in your own package %%: How to ?.String manipulation with stringi package.Standardize analyses by writing standalone R scripts.Reshaping data between long and wide forms.Reading and writing tabular data in plain-text files (CSV, TSV, etc.).Non-standard evaluation and standard evaluation.Network analysis with the igraph package.Implement State Machine Pattern using S4 Class.I/O for geographic data (shapefiles, etc.).I/O for foreign tables (Excel, SAS, SPSS, Stata).Feature Selection in R - Removing Extraneous Features.Extracting and Listing Files in Compressed Archives.Date-time classes (POSIXct and POSIXlt).Empirical Cumulative Distribution Function.*apply family of functions (functionals).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
